This post first appeared on Risk Management Monitor. Read the original article.
Summer has arrived, but it is not a time for total relaxation. According to the National Safety Council (NSC), July and August typically see more accidental deaths than any other two-month period—a trend that includes drowning, pediatric vehicular heatstroke, pedestrian deaths, natural disasters and gun-related fatalities.
To stress the need for extra caution, the NSC has updated its Injury Facts interactive online database. This year marks the first time the NSC has categorized “hot car deaths” – which it recognizes as an emerging risk.
“Unfortunately, when we look at accidental deaths, summer is not the carefree period we’d like it to be,” NSC Manager of Statistics Ken Kolosh said. “The numbers underscore the need for public awareness. We hope Injury Facts can help people understand the biggest risks to their safety and take the steps needed to ensure no one gets hurt.”
With Independence Day arriving next Wednesday, more workers are expected to travel and take time off from their jobs. With an increase of people on the road and in pools and oceans, for example, more people are at risk of injury or death.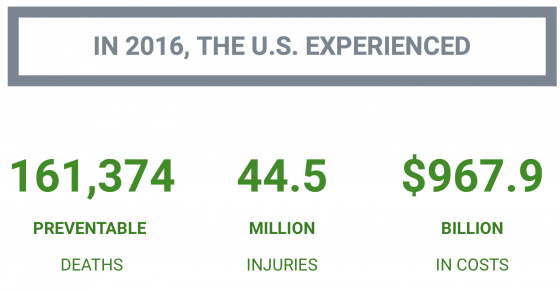 The NSC information released earlier this week dovetails with the end of National Safety Month. Facts and trends include:
The NSC information released earlier this week dovetails with the end of National Safety Month. Facts and trends include:
- Pedestrian fatalities. Pedestrian deaths start to increase in late summer and continue a steady increase through the end of the year. Since 2009, pedestrian deaths have risen sharply, totaling 7,330 in 2016 compared to 4,109 in 2009. For the first time, Injury Facts shows where pedestrian fatalities tend to occur, outdoor lighting conditions at the time of the death and the day of the week the incident occurred.
- Drownings. Swimming, playing in the water or falling in the water claimed 656 lives in July alone in 2016, a 108% increase over the yearly average and their highest level that year. In total, 3,786 people died in 2016 from drowning. Injury Facts now breaks down all preventable deaths by month so people understand the biggest risks facing them throughout the calendar year.
When chronicling drunk driving incidents, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) is pointing out the deadliness of the four-day period between July 2 and July 6. Over the 2016 Fourth of July holiday:
- 188 people were killed in crashes involving at least one driver or motorcycle operator with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of .08 or higher. (A 28% increase from 2015, which had 146 fatalities).
- Nearly half of those who died were in a vehicle crash involving at least one driver or motorcycle operator with a BAC of .15 or higher—almost twice the legal limit.
Even if you’re off the road and hosting a company party or celebrating in a backyard, there are risks all around. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) warns that there are more fires reported on the Fourth of July than any other day of the year, nearly half of which are caused by fireworks. With extreme drought plaguing the western states, fireworks, outdoor grilling areas, and campfires require extra caution. The NFPA said that July is the peak month for grilling fires, with gas leaks cited as the leading cause.
And while looking to the sky for a fireworks show is always fun, the aforementioned groups recommend attending displays put on by professionals only and avoiding consumer fireworks. According to the Consumer Product Safety Commission’s (CPSC) 2017 Fireworks Annual Report, fireworks were involved in an estimated 11,100 injuries treated in U.S. hospital emergency departments in 2016.
“Preventable injuries are the third leading cause of death for the first time in United States history,” NSC President and CEO Debbie Hersman recently told Risk Management Monitor. “Sadly, our national opioid epidemic and the sudden recent increase in motor vehicle deaths have propelled preventable injuries past chronic lower respiratory disease and stroke in terms of how many lives are lost each year. Every single unintentional injury could have been prevented.”

